Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics
Click2Drug
Directory of computer-aided Drug Design tools
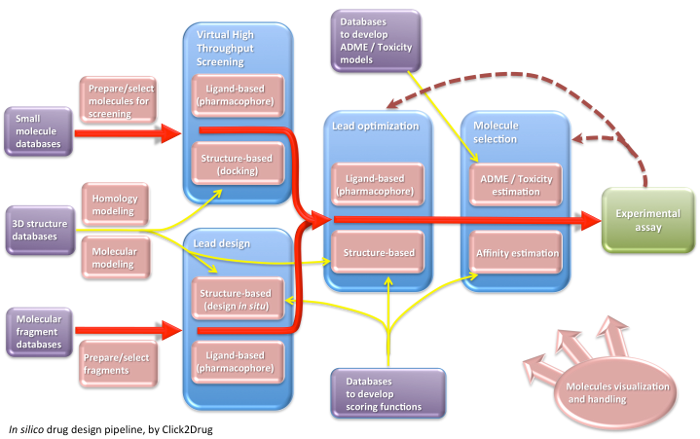
Click2Drug contains a comprehensive list of computer-aided drug design (CADD) software, databases and web services. These tools are classified according to their application field, trying to cover the whole drug design pipeline. If you think that an interesting tool is missing in this list, please contact usClick on the following picture to select tools related to a given activity:
Show all links Hide all links
Screening
Software
- MedChem Studio. Cheminformatics platform for computational and medicinal chemists supporting lead identification and optimization, in silico ligand based design, and clustering/classifying of compound libraries. It is integrated with MedChem Designer and ADMET Predictor. Distributed by Simulation Plus, Inc.
Ligand design
Software
- BREED. Program for ligand-based ligand design, by hybridization of known ligands. Distributed by Schrodinger.
- LeadGrow. Provides features for focused combinatorial library generation and screening to grow a lead molecule and perform lead optimization. Provides Lipinski screen and activity prediction using pre-generated QSAR models. Provided by VLife.
- Phase. Program for ligand-based drug design using pharmacophore modeling. Distributed by Schrodinger.
- CoLibri. Assembles huge compound collections from multiple sources and various input formats into a virtual screening library, removes duplicates, assesses the distribution of physico-chemical properties of the compounds and makes selections/filter based on any property-threshold, molecules name-pattern or presence/absence of a particular substructure motif. Generates fragments library. Modifies molecules or fragments for generating, transforming and general handling of virtual screening libraries. Distributed by BioSolveIT.
- ReCore. Replaces a given pre-defined central unit of a molecule (the core), by searching fragments in a 3D database for the best possible replacement, while keeping the rest of the query compound. Additionally, user-defined "pharmacophore" constraints can be employed to restrict solutions. Distributed by BioSolveIT.
- LigMerge. Program combining structures of known binders to generate similar but structurally distinct compounds that can be tested for binding. Free and open source. Distributed by the National Biomedical Computation Resource.
- MedChem Studio. Cheminformatics platform for computational and medicinal chemists supporting lead identification and optimization, in silico ligand based design, and clustering/classifying of compound libraries. It is integrated with MedChem Designer and ADMET Predictor. Distributed by Simulation Plus, Inc.
- LoFT. Tool for focused combinatorial library design using a (ligand-based) weighted multiobjective scoring function based on physicochemical descriptors.
- ACD/Structure Design Suite. Helps chemists optimize the physicochemical properties of their compounds. The software suggests alternative substituents (at a site/sites on the molecule) to drive the property of choice in the desired direction. Helps adjust aqueous solubility, lipophilicity (logP or logD), or change the ionization profile (pKa) of molecules. Distributed by ACD/Labs.
- CoG. Program for ligand-based ab initio ligand design, using a graph-based genetic algorithm.
- Flux. Program for ligand-based ligand design using a EA approach.
- ilib diverse. Program for creating virtual libraries of drug-like organic molecules suitable for rational lead structure discovery. Ligands are designed by combining user-defined fragments according to state-of-the-art chemical knowledge. Generated compounds can be filtered according to a variety of physico-chemical filters. Developed by inte:ligand.
- EMIL. (Example Mediated Innovation for Lead evolution). Suggests chemical modifications to hits to turn them into bona fide leads. EMIL searches through its Knowledge Base looking for similar chemistry and how it was optimized for potency and bioavailability (Iientification of bioisosteric/bioanalogous structures, indication of empirical information of the modification, such as change in physicochemical, in vitro and in vivo effects, etc...). Distributed by CompuDrug.
- Legio. Indigo-based GUI application that exposes the combinatorial chemistry capabilities of Indigo. Free and open source. Distributed by GGA software.
Databases
- SwissBioisostere. Freely available database containing information on millions of molecular replacements and their performance in biochemical assays. It is meant to provide researchers in drug discovery projects with ideas for bioisosteric modifications of their current lead molecule, and to give access to the details on particular molecular replacements. Users can provide a molecular fragment and get possible replacements, along with the biological assays in which they were observed. Users can also provide a given molecular replacement and get the corresponding information. The data were created through detection of matched molecular pairs and mining bioactivity data in the ChEMBL database. Developed and maintained by Merck Serono and the Swiss Institute of BioInformatics.
- VAMMPIRE. (Virtually Aligned Matched Molecular Pairs Including Receptor Environment) matched molecular pairs database for structure-based drug design and optimisation. By building MMPs between PDBbind and ChEMBLdb ligands VAMMPIRE extrapolates the two-dimensional ChEMBLdb ligands to the assumed, three-dimensional binding mode and introduce the received binding information into the database. Provided by the Institute of Pharmaceutical Chemistry / Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany.
- sc-PDB-Frag. Database of protein-bound fragments to help selecting truely bioisosteric scaffolds. The database allows to (i) search fragment among PDB ligands or sketch it; (ii) define similarity rules to retrieve potential bioisosteres; (iii) score bioisosteres according to interaction pattern similarity; (iv) align bioisosteres to the reference scaffold; (v) Visualize the proposed alignment.
ADME Toxicity
Software
- MedChem Studio. Cheminformatics platform for computational and medicinal chemists supporting lead identification and optimization, in silico ligand based design, and clustering/classifying of compound libraries. It is integrated with MedChem Designer and ADMET Predictor. Distributed by Simulation Plus, Inc.